Let’s Discuss the Difference between Mental and Behavioral Health

You may have come across the term “behavioral health” while investigating mental health treatments. The phrase “behavioral health” was coined forty years ago, although its definition has evolved over time.
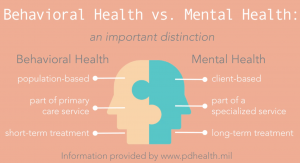
People nowadays commonly confuse behavioral health with mental health, but the truth is that there is a distinction between the two. Understanding the distinction is crucial to receiving the proper treatment for your ailment.
Your health can be influenced by a variety of factors, including sleep, nutrition, and exercise. While we frequently focus on our physical strength, there’s another crucial aspect of our well-being to consider: how we think, feel, and act. These have to do with your mental and behavioral wellness.
While many individuals use these phrases interchangeably, there are important distinctions to be aware of while diagnosing and treating psychological problems. There are also diverse techniques to dealing with behavioral health and mental health issues.
You can benefit from knowing the difference between these two concepts whether you want to better understand your own psychological well-being or help others take control of theirs. Join us as we learn the differences between the two, as well as some prevalent symptoms, and treatments related to each.
Which is Which? Basic Definitions
Behavioral health is a broad term that refers to how a person’s actions affect their overall health. This covers mental health and substance misuse concerns, stress-related physical symptoms, and health-related behaviors. Weight loss, smoking cessation, and pain management are examples of behavioral health concerns.
Our emotional, psychological, and social well-being are all addressed by mental health. Some aspects of mental health, according to the US Department of Health and Human Services, include:
- What we believe, feel, and do
- How we deal with stress
- How we interact with others
- How we make decisions
The World Health Organization defines mental health as “a condition of well-being in which each individual fulfills his or her own potential, can cope with typical stressors of life, can work successfully and fruitfully, and can contribute to his or her community.”
Your mental health is influenced by a variety of things, including your biology, psychological state, and behaviors. Your behavioral health, on the other hand, dictates how your habits affect your physical and emotional health.
Related Post: Importance of mental health
The Most Common Behavioral Health Disorders
Simply put, behavioral health is concerned with how our daily cognitive habits influence our behavior, wellbeing, biology, and emotions. Behavioral health is more extensive when compared to mental health. This is due to the fact that it concerns how our thoughts, activities, and mental health affect our entire well-being.
When someone’s mental and behavioral health is in good shape, they will act in ways that help them maintain a good balance between their physical and mental health. In other words, for the management of an existing injury or health problem, there will be a balance in the utilization of a balanced diet, exercise, and other healthy habits.
The following are a few examples of frequent behavioral health disorders:
Substance Abuse – When a person misuses substances, it is referred to as substance abuse. It could be a coping method or self-medication for an existing condition. Substance misuse exacerbates any existing problem that a person may be coping with over time.
Self-Injury – Self-injury is a condition in which a person injures themselves as a result of having a bad self-image. Some of the risk factors for self-injury include disassociation and despair.
Addiction to Gambling – This condition develops when a person has a compulsive need to gamble despite the negative consequences of doing so.
Eating Disorders – These are classified into several categories. Some of the most prevalent forms include binge eating, bulimia nervosa, and anorexia nervosa. Any of these eating disorders can lead to serious medical problems like obesity, unhealthful weight loss, and mental health problems.
Treatment for Behavioral Health
Behavioral health, like mental health, is primarily treated through therapy. The therapy process usually entails the individual’s ability to learn how to control the behaviors associated with mental illness, as well as encouraging individuals to challenge themselves to improve their behaviors by reinforcing positive behaviors and overcoming negative ones.
The Most Common Mental Health Disorders
Mental health, on the other hand, is the relationship between a person’s well-being and their environment, biology, and habits. Although mental health is frequently defined as behavioral health, it is important to clarify that this word does not specifically focus on an individual’s activities.
Simply defined, behavioral health is concerned with the implications of a person’s activities on their well-being, whereas mental health is concerned with a person’s overall state of being.
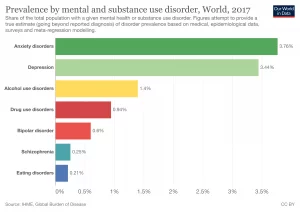
source: https://ourworldindata.org/mental-health
Here are some of the most frequent mental health issues that people face:
Depression – It is a mood illness in which people experience feelings of being heavy and empty from time to time. This ailment has an impact on the affected person’s day-to-day existence. Depressions such as seasonal affective disorder and postpartum depression are frequent.
Bipolar Disorder – It is a mental illness that manifests itself as a series of bouts of intense hyperactivity and despair. Because the severity of the bipolar disorder varies from person to person, each person will have a unique experience.
Anxiety – Unlike the occasional anxiety that most individuals feel, generalized anxiety disorder entails chronic worries that interfere with a person’s day-to-day existence. This disorder has no recognized cause in certain cases and can progress to panic disorder.
Schizophrenia – Despite the fact that this disorder is not prevalent, its consequences are often seen in those who are affected. Unhealthy and recurrent thoughts, hallucinations, and delusions are some of the symptoms.
Treatment for Mental Health
Treatment for mental illness varies depending on the diagnosis you currently have. This might comprise a variety of services, the most common of which is treatment. Therapy for mental health usually focuses on furthering your understanding of your ideas, feelings, and behaviors, with the goal of improving an individual’s well-being.
The most effective strategy to improve healing is to combine psychotherapy with medicine. Cognitive-behavioral therapy, exposure therapy, dialectical behavior therapy, and other therapies are some examples. Art therapy, as well as other holistic treatments like reiki or guided imagery, can be used in therapy.
Medication may be used as part of the treatment, which should be discussed with a medical practitioner because pharmaceuticals may work for some people but not for others, and it may take some time to acclimatize to the meds provided, depending on the individual.
It is critical that you communicate with your doctor to identify any side effects you may be experiencing, such as exhaustion, loss of appetite, or increased anxiety.
Peer support and support groups having the capacity to connect with individuals who have gone through similar things and can provide emotional and physical support can be quite valuable during this time.
The Link between Behavioral Health and Mental Health
Even though harmful habits are a hallmark of behavioral health issues, they are rarely the source of the problem. Behavioral health issues frequently coexist with mental disease. It is not enough to just modify behaviors to properly cure any of these illnesses; you must additionally consider psychiatric therapy and/or psychological counseling to address the underlying problem.
While many mental health issues have a biological basis, your activities can still have a significant impact on them, both positively and negatively. Drinking, using drugs, or overeating are all examples of maladaptive habits that can increase the symptoms of a mental health issue.
Developing appropriate coping methods, such as exercising or meditating, on the other hand, can benefit both your physical and mental health.
Positive activities may assist to lessen the effects of a mental illness. Meditation, exercise, and socializing with friends are all good ways to improve your mental health. Similarly, treating a mental health problem may assist a person in achieving a state that permits them to develop better behaviors.
Getting the Correct Diagnosis and Treatment
No matter if you’re concerned about your mental health, behavioral health, or both, it’s vital to get the correct diagnosis for your condition. Inexperienced caregivers may place a greater emphasis on behavior modification while disregarding underlying psychiatric concerns or treat a mental disease with medications while ignoring the need to change bad habits.
A collaborative approach, with a team of professionals taking into account all aspects of a patient’s health, is the most effective treatment plan. Medical therapies, cognitive behavioral therapy, group counseling, and other treatments are commonly employed.
When a behavioral health problem, such as substance abuse, co-occurs with a mental health issue, collaborative care is crucial. Working together, a multidisciplinary team of doctors and therapists can guarantee that a patient receives the finest possible care to help them live their best life.
Even for trained mental and behavioral health experts, determining whether a person has mental health disorders or is merely dealing with a behavioral health condition can be challenging.
The diagnosis procedure must include a thorough examination of the individual’s life history, the underlying reason for their present health crisis, and their current demands.
For example, if a person has a severe opioid addiction, the addiction may have begun as a result of managing chronic pain. However, additional investigation reveals that the discomfort may have been caused by sexual abuse. In this instance, all facets of the individual’s health must be addressed.
More Care than Cure – How Every Patient’s Needs Vary
Every person’s requirements are unique. One of the most important aspects of the care that a healthcare provider must give is an individualized treatment plan that addresses an individual’s frequently complicated needs. This could entail simultaneously addressing mental illness and behavioral health issues.
Good healthcare providers can help design a plan that addresses all areas of an individual’s needs through collaborative care, especially when co-occurring illnesses are present.
This could entail detoxing from any substances that have been present. It’s often the initial step, and it can help reveal any underlying mental health issues the person is dealing with.
A treatment plan for persons with mental health disorders may involve drugs to assist stabilize the illness so that treatment and therapy can continue.
Individuals with behavioral health illnesses who are on their own may need to pursue a variety of therapy options, both residential and outpatient, in order to receive non-medication treatment.
Counseling, both group and individual, is often an important part of treating mental and behavioral health conditions. Individuals also benefit from holistic care because it allows their bodies to heal, which have been abused and injured as a result of chemical addiction or poor mental health issue management. In every case, a personalized treatment plan becomes the best solution.

